Last updated: December 30th, 2023
The California earthquakes in July 2019 reinforced the reality that earthquakes can occur at any time. While no one can predict when a major quake will hit the state, it poses a potential risk of serious damage to structures. Although we can’t prevent earthquakes, securing your garage and home can help reduce their impact.
How to Prep Your Garage for an Earthquake
In the following section, we explore possible weaknesses in the garage and discuss how to address them.
1. Identify and Fix Walls Weakness in the Garage
The garage can potentially be one of the more significant vulnerabilities a home has during a seismic event. The large opening of a garage door reduces the garage’s structural support. This could be especially problematic if there’s a room or structure above the garage, as the walls may be too weak to withstand the shaking from the quake. See Fig. 1.
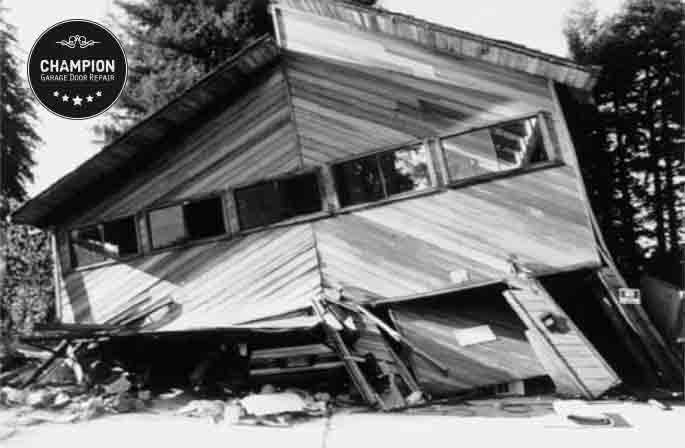

You may need to retrofit your garage by bracing your garage door opening if the garage has no in-line wall with the rest of the house. For example, the house configuration in Fig. 2, left side, will require reinforcement and bracing for the garage door opening, as the garage walls are not in line with the rest of the house.
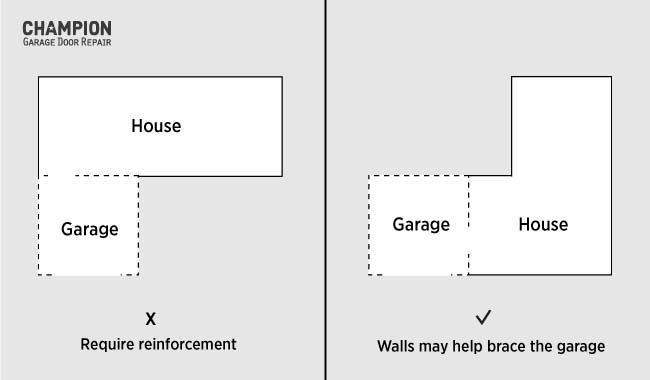
The reinforcement and bracing are accomplished by adding plywood panels and steel straps around the garage door opening. The project cost is estimated to be between $5,000 and $20,000.
2. Identify and Fix Weaknesses with the Garage Door
A garage door and hardware that are not properly secured may not hold during a significant seismic activity. Inspect the garage door supporting brackets and end plates. You can reinforce the hardware to the garage frame by using 6” lag bolts instead of the standard 3”. Additionally, you can replace the standard punched angles with heavy-duty ones to better secure the garage door tracks to the rafters, although the standard punched angles are usually strong enough.
Another important step is to ensure that the electric garage door opener is properly mounted to the ceiling or rafters. A weak garage door opener mounting bracket during a quake not only could cause damage to vehicles and belongings but also poses a fire hazard.
If the garage door opener was purchased and installed by home improvement retailers, it is recommended to have a licensed garage door repair contractor inspect and secure it properly. Retailers often outsource their garage door projects to gig workers who use generic steel straps supplied by the retailer, which might not hold during a major earthquake.
The project cost is estimated to be between $300 and $1,200.
3. Secure Objects in the Garage
Water heaters should be braced and secured using straps and screws. You can use any strap kit or bracing kit from a local hardware store or contact a licensed plumber. Ensure that the screws are secured into the studs, not just the drywall.
Use flexible pipes for electrical, gas, and water lines. Flexible pipes are a safer alternative to the standard rigid pipes during an earthquake.
Ensure that shelving and storage units are properly secured to the rafters, studs, or floor to prevent them from collapsing or falling over. Additionally, securing heavy items in position will keep them from crashing down during a powerful quake.
Keep breakable items stored on lower shelves. Use latches to secure cabinet doors and keep them closed. Flammable products and those containing chemical ingredients should also be stored on lower shelves, preferably secured in closed cabinets.
The project cost is estimated to be between $50 and $1,500.
4. Keep you Garage Door in Good Repair
Maintaining, inspecting and testing your garage door regularly not only ensures compliance with applicable mandatory and advisory safety requirements and regulations but also reduces the risk of costly damage, increasing the chances of it withstanding a significant earthquake.
The recommended garage door maintenance cost is estimated to be between $150 and $300.
The Ridgecrest Earthquakes
On the Fourth of July, 2019, Southern California experienced a magnitude 6.4 earthquake at 10:33 in the morning. The tremor was felt as far as Long Beach, Reno, Las Vegas, Nevada, and Phoenix, Arizona. A stronger aftershock, measuring magnitude 5.4, occurred the next morning.
A more powerful earthquake, measuring magnitude 7.1, struck Searles Valley on July 6th. Approximately 15 million people felt the effects of this tremor.

Governor Gavin Newsom declared a state of emergency, emphasizing that the July earthquakes were a wake-up call. It’s not only residents who need to make changes for better earthquake preparedness; the state government is investing over $40 million to expend its warning system. This includes allocating $16 million to install sensors designed to detect seismic activity moments before a quake strikes. The implementation of this early warning system will enable the safe shutdown of trains and utilities ahead of significant shaking, aiming to protect infrastructure and reduce injuries.
Know the Magnitude Risk
Earthquake intensity is measured using a magnitude scale, a unit of measurement capable of detecting even the most minor quakes. Below, we list the Earthquake Magnitude Scale that scientists use for assessing the possibility of damage and injury:
- 5 or less magnitude: Usually not felt, but can be recorded by seismograph.
- 5 to 5.4 magnitude: Often felt, but only causes minor damage.
- 5 to 6.0 magnitude: Slight damage to buildings and other structures.
- 1 to 6.9 magnitude: May cause a lot of damage in very populated areas.
- 7.0 to 7.9 magnitude: Major earthquake. Serious damage.
- 8 or greater magnitude: Great earthquake. Can totally destroy communities near the epicenter.
Various factors can influence the damage and injuries caused by earthquakes. Despite experts estimating damage for each magnitude, buildings, old or new, can be vulnerable even to minor quakes. When evaluating potential damage, these additional factors are also considered.
- Distance from the earthquake: Those closer to the quake’s epicenter will feel its effects more intensely. Other variables, such as if the earthquake occurred offshore, also influence the strength of the effects.
- The Ground Soil: The type of soil in your surrounding area affects how strongly a quake impacts an area. Looser soil transmits ground waves better than rock or tightly compacted earth.
- Building Construction: Older buildings and structures were constructed before proper standards were in place, rendering them less likely to withstand higher-magnitude earthquakes.
Is Your Garage and Home at Risk of Earthquake Damage?
Your garage and home face lateral (side-to-side) and uplift (up-and-down) forces during earthquakes. New building codes require stronger structures using a “continual load path,” ensuring robust connections throughout.
These connections redistribute forces during earthquakes, improving a structure’s ability to withstand seismic activity. Check if your garage needs retrofitting:
- Living in a seismic area (e.g., California): Retrofit if in Seismic Zone 3 or 4.
- Home older than 20 years: Older homes may lack earthquake-resistant features.
- Raised foundation homes: “Cripple walls” may be insufficient during seismic events.
- Homes with space above the garage: Insufficient support can cause detachment and collapse.
How Retrofitting Your Garage and Home Can Impact Their Value?
Research using real estate sales listings and other public data suggests that seismic retrofitting of your garage and home increases the home’s resale value by 9.85%, a figure significantly higher than the average cost to perform the retrofit work by licensed contractors. This value increase is even greater when paired with the potential savings from an earthquake repair.
Retrofitting Costs Compared to Repairs
In a case study conducted by APA The Engineered Wood Association, an architect who participated in the research and owned both a retrofitted and non-retrofitted property reported incredible findings. After the 7.1 magnitude Loma Prieta earthquake, the architect incurred a repair cost of $5,000 for the retrofitted building, whereas the non-retrofitted building faced repair costs totaling a staggering $260,000.
When considering garage doors, the average cost for retrofitting and repairing one is approximately $500. However, replacement and installation expenses of a complete electric overhead door system can vary between $2,500 and several thousand dollars. The total depends on factors such as door size, type, design, and materials.
Preparing Your Garage and Home for an Earthquake
Start by identifying hazards in your home, ranging from minor issues with simple fixes to those that require more involved solutions. Collaborating with qualified engineers and licensed garage door repair companies to assess and eliminate potential weaknesses can significantly reduce the risk of physical harm to you and your loved ones, as well as property damage.
California homeowners can apply for grants of up to $3,000 through EBB programs to retrofit older single-family homes. Check the Earthquake Brace + Bolt website for more details.
In addition to securing your garage door and home, knowing what to do if an earthquake strikes can mean the difference between life and death.




Wow! This one is the best! I accidentally visited this site while looking for something else!, But Wow!, Good thing I came into this site. Thank you for sharing this guide with us, it is really helpful!